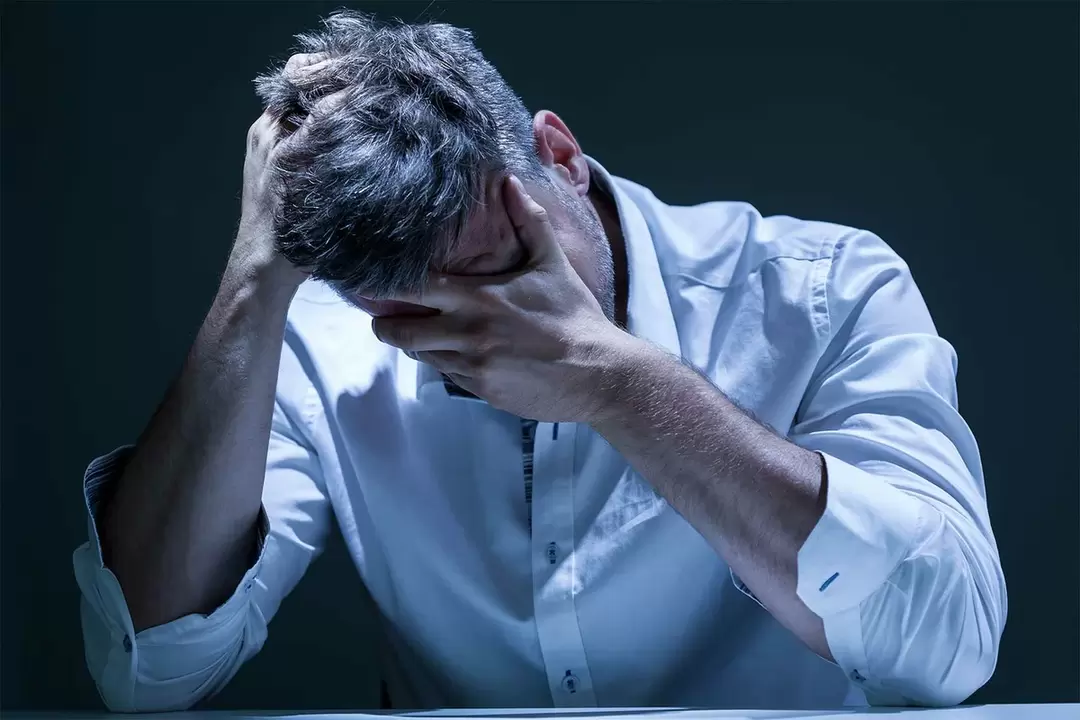
The term "prostatitis" refers to a chronic or acute inflammatory process of any etiology occurring in the prostate gland. Since the prostate is a male-specific organ, prostatitis develops only in men. There are many types of prostatitis, but any type of prostatitis can be divided into acute and chronic.
Acute prostatitis occurs under the influence of many factors - the presence of bacteria, viruses, protozoa, under the influence of malnutrition, sedentary lifestyle, bad habits and other factors. another factor. >
The prostate gland is an exocrine gland, i. e. secretions that it secretes into the external environment. In humans, the prostate is an unpaired organ whose activity is dependent on male sex hormones, namely androgens and steroids.
The prostate gland is located behind the bladder, hugging the original part of the urethra, where its ducts open.
It is in its place that the prostate gland has one of its functions - during an erection it blocks the exit from the bladder. It is the prostate gland that is responsible for the sensation of orgasm, which occurs due to the gland's abundant supply of nerves, i. e. the innervation.
Temperature
One of the first signs of acute prostatitis, whatever its cause, is an elevated temperature. As with any other inflammatory process that occurs in the body, the temperature rises to a sub-threshold - that is, about 37. 5-380ARE FROM.
Furthermore, the more intense the immune response, i. e. the body's response, the higher the temperature rise. That is, in the advanced stages of the disease, the body temperature can rise up to forty degrees.
Naturally, just an increase in temperature cannot indicate the presence of prostatitis.
Usually, the first symptoms of prostatitis are difficulty urinating when additional muscles are used - the abdominal muscles, violation of the ejaculatory mechanism, itching, burning and other discomforts in the perineum orgenitals.
Go to the toilet often
In addition, this is an increase in the desire to urinate (with a small amount of urine being passed out), a "residual urine" feeling after emptying the bladder, an unpleasant orgasm, and the result. is a decrease in sex drive.
General weakness
As with any other inflammatory disease, there is a toxic syndrome, which includes general weakness, decreased performance, nausea, and possibly vomiting.
There are also disorders of the nervous system - depression, irritability and others.
What causes prostatitis?
There are also predisposing factors to prostatitis - hormonal imbalance, including age, prolonged sexual abstinence, smoking, general hypothermia, stool retention, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity, overheating, history of chronic sciatica, immunocompromised state, age-related changes in body composition.
Particular attention should be paid to a predisposing factor such as inflammatory diseases of the kidney and urinary tract, as infection can spread upward.
It happens that the disease begins with urethritis
The early stages of prostatitis are characterized by a rather typical clinical picture - lethargy urine stream, frequent urination, fever. There may be pain in the perineum. Often there is a violation of sexual function.
However, sexual dysfunction tends to be psychological, circulatory, or clinical. The process of ejaculation itself does not bring pleasure at all, even causes pain, thereby forming a conditioned reflex that leads to a decrease in desire.
In purely physiological terms, prostatitis can lead to incompetence only in the late stages. The initial phase is also known as the "first sign" phase - the onset of urination doesn't happen immediately, as it usually does, but with a slight delay.
Already at this stage, the prostate gland has enlarged, but is not painful to palpation. Simultaneously, the contours of the prostate are clearly palpated, and the median border is also palpated - as in the norm. The most interesting thing is that the period of the first signs can last quite a while - up to three years.
Patients of urologists in recent years have increasingly become young people. That is, the more inflamed the prostate gland "rejuvenates". This is due to the proliferation of "outrageous" forms of recreation - surfing, diving, skiing and kayaking. When there is insufficient intake and the body cools down completely, prostatitis can occur.
And paradoxically, too "calm" lifestyle can also lead to the development of prostatitis. It is due to stagnant blood and lymph in the pelvis - a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle is not the best way to disperse blood in the organs.
Inflammatory diseases that are not fully cured, which may be completely unrelated to the pelvic organs, are also predisposing factors for prostatitis. This is due to the fact that infection (of any cause) from the primary focal point can enter the prostate by blood or lymphatics. When there is a blockage in the pelvis, the infection settles there and begins to multiply.
It also happens that prostatitis occurs due to stress. Stress weakens the immune system, thereby increasing the risk of prostatitis.
STDs - "sexually transmitted diseases" - are one of the main causes of prostatitis. Gonorrhea, if not treated properly, almost always causes prostatitis.
However, do not forget that one cannot go from one extreme to another. If you abstain from sex for a long time, it will again form a stagnation of blood and lymph in the pelvic organs, stagnation of secretions in the prostate gland, thereby leading to prostatitis.
The prognosis for timely detection and adequate treatment of this disease is favorable, however, if the disease becomes chronic or has secondary infection, it will entail rather sad consequences.